The Device Install Kit download site does not provide access to all Emerson Process Management device files. Device files distributed on DeltaV and AMS Device Manager release media are not duplicated for download from this site. NI Device Drivers provides popular NI instrument drivers you can use to control NI and third-party hardware. NI Device Drivers is a bundle that features most NI instrument drivers, including NI-DAQmx, NI-VISA, NI-SCOPE, and NI-SWITCH.
- Download U-blox Usb Devices Driver Download
- Download U-blox Usb Devices Driver Updater
- U-blox 7 Download
- U-blox 7 Driver
Installing the u-blox USB drivers for Windows for use with RTKLIB can be a little tricky now that u-blox has switched their default Windows configuration from using COM port drivers to using sensor device drivers. RTKLIB does not support sensor device drivers, so it is necessary to force the driver installation process to revert to a driver that supports the COM port interface.
To make things more confusing, there are actually three different drivers that will support the COM port interface. You can determine which driver you are using by opening the Windows Device Manager while the u-blox reciever is plugged into the computer. The receiver will either show up under “Ports” or under “Sensors”. If it shows up under “Sensors” then RTKLIB will not be able to see it. Here is an example of what it looks like when it shows up under “Ports”:
If it shows up under “Ports” it may be listed in one of three different ways depending on which driver is installed. They are:
USB Serial Device (COMx): This is the generic COM port Windows driver and is what u-blox recommends for Windows 10 when using the COM port interface. It will work fine with RTKLIB, but Windows has an annoying habit of automatically replacing it with the sensor driver, so I have recently stopped using this one.
u-blox Virtual COM Port (COMx): This is the driver recommended by u-blox if you want to support both the sensor interface and the COM port interface. It has some limitations though, the primary one being that you can only run one of these devices on a computer at a time, so I don’t recommend this one either.
u-blox GNSS Reciever (COMx): This is the older u-blox driver before they switched to the sensor interface. U-blox recommends this for older versions of Windows but I have started using this recently with Windows 10. So far I have found it works fine, and it does not automatically get replaced by Windows like the generic driver does. I recommend this one.
All three u-blox drivers are available for download from their Product Resources page. The older driver is listed as “u-blox GNSS Standard Driver for Windows”. U-blox has published a flowchart on their website to help users decide which driver to use and how to rollback to older drivers. Here is a copy of the document but it may be too small to read here and may be out of date by the time you read this so I suggest you click on this link to take you to the original document.
To revert to the generic Windows driver with Windows 10, follow the instructions in the blue circle above. To revert to the older u-blox driver with Windows 10, you will want to first download that driver from the u-blox Product Resource page, then follow the instructions inside the blue circle.
≡ PagesFavoritedFavorite2Introduction
Download U-blox Usb Devices Driver Download
U-center from u-blox is a free software tool for configuring u-blox GPS receivers under Windows. U-center is a dense program with many interface elements. It can be overwhelming at first but over time it will become easier to use. For all its GUI weaknesses, it is very powerful for configuring the u-blox line of modules (such as the NEO-M8P-2 and SAM-M8Q to name a few). In this tutorial, we will be exploring some of its features with the NEO-M8P-2.
Required Materials
To follow along with this tutorial, you will need the following materials. You may not need everything though depending on what you have and the design of the u-blox's board. We'll be using the NEO-M8P-2 throughout this guide. Feel free to add it (or another u-blox module) to your cart, read through the guide, and adjust the cart as necessary.
GNSS Multi-Band Magnetic Mount Antenna - 5m (SMA)
GPS-15192SparkFun GPS-RTK Board - NEO-M8P-2 (Qwiic)
GPS-15005 6
6Download U-blox Usb Devices Driver Updater
USB micro-B Cable - 6 Foot
CAB-10215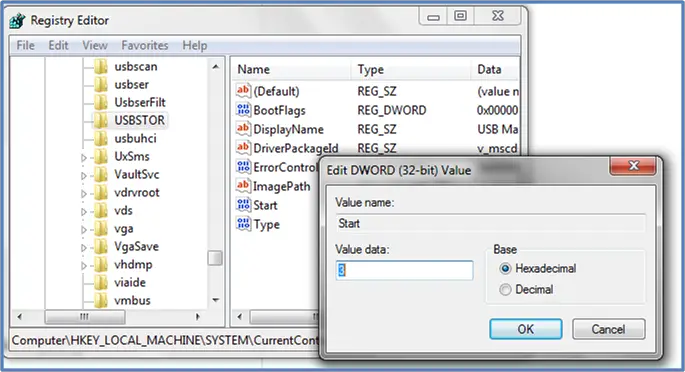
Interface Cable SMA to U.FL
WRL-09145Required Software
The software can be obtained from u-blox. To follow along with this tutorial please download and install u-center. Once completed, open it.
Install Drivers
For this tutorial we'll assume you have the SparkFun GPS-RTK but u-center can be used with any u-blox based product. Start by attaching a micro-B cable to the GPS-RTK board.
Now open Windows Device Manager. The NEO-M8 series has an annoying feature where the module comes up as a Windows Sensor rather than a serial device. If your u-blox receiver does not appear under COM ports then right click on the u-blox GNSS Location Sensor and then Update Driver. Next, click on Browse my computer for driver software.
Then “Let me pick”...
Select the first USB serial device.
The SparkFun GPS-RTK board should now enumerate as a USB serial COM port. In the list below, the GPS-RTK board is COM12.
Return to u-center and drop down the port list. Select the COM port that is your RTK board. Congrats! You can now use u-center.
Configuring and Outputting NMEA Sentences
Let’s go over a few features you’ll likely use:
Text Console
The text console button will show you the raw NMEA sentences. This is handy for quickly inspecting the visible ASCII coming from the module over USB.
Configure
The configuration button opens the most powerful window. From this window you can inspect and configure new settings. It’s not obvious but when you click on a setting such as ‘MSG (Messages),’ u-center will poll the module for its current state. The ‘10s’ in the corner indicates how old the displayed information is. In this case it’s been 10 seconds since this setting was last queried. Click on the ‘Poll’ button to update the information. Go ahead and select the F0-00 NMEA GxGGA message. As you click the dropdown menu, the software will poll the current settings. It’s a bit disorienting at first but gets better over time.
The MSG configuration is very powerful. It allows you to enable or disable various NMEA sentences as well as binary protocols such as NAV-PVT (checkout the full protocol datasheet). Once a sentence is selected, such as GxGGA, the check boxes will be populated. If you want to disable the GxGGA sentence for the SPI interface, uncheck the SPI checkbox and then click ‘Send’. Congrats! The GxGGA sentence is no longer presented on the SPI interface. This raises an important fact:
Note: The NEO-M8 series has 4 interfaces: USB(serial), I2C, SPI, and UART. All interfaces can access information simultaneously. This means you can inspect configuration settings over the USB serial port while your Arduino makes setting changes over the I2C port. You can read NMEA sentences over the I2C port or send RTCM data into the module over SPI. It’s all highly configurable.
What is the USB Port on the NEO-M8P?
It’s like any other USB to serial device. It will enumerate on your computer as a COM port and acts as such. It is independent and separate from the UART port that is a dedicated TTL serial port.
If something is not accessible through u-center, it probably means that feature or setting is not compatible with the currently attached device. For example, the UART2 box is grayed out in the image above. The NEO-M8P does not have a second UART so you can’t address it.
Ports
The Ports (PRT) sub-menu under Configuration is very helpful. You can do things like change the baud rate, I2C address, and protocols. Depending on your application, you may want to enable or disable entire interface protocols. For example, if you want to enable NMEA sentences for the SPI interface, you would do it here. Fortunately, the factory default for the NEO-M8P is good for I2C and UART1 for RTK purposes (input of RTCM3 is enabled for both ports).
This is also the menu that allows you to change the I2C address of your GPS-RTK. Because we are big fans of the Qwiic system, we’ll be using the GPS-RTK on the I2C bus. If we had another device on the bus that uses address 0x42 this menu will allow us to change the address of the GPS-RTK.
Poke around the various config menus. If you get your module into an unknown state you can unplug and replug to reset the settings.
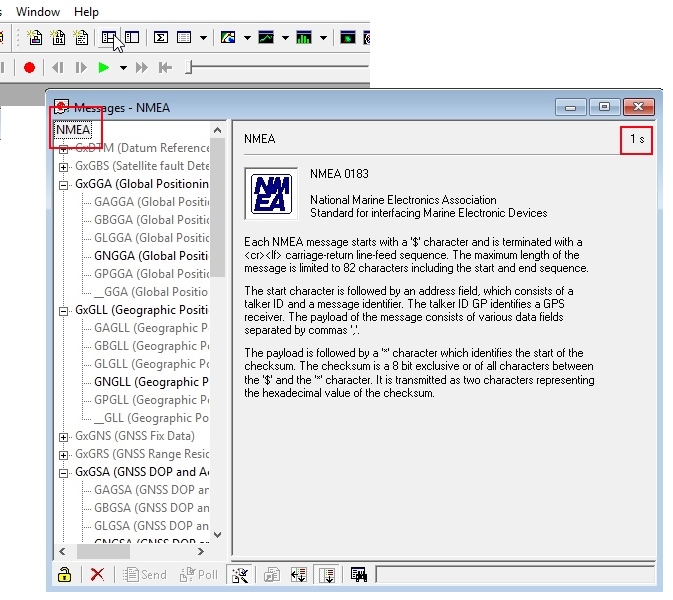
Messages
The messages window will allow you to view the various sentences reported by the module. It’s not obvious but if you double click on ‘NMEA’, the tree of messages will fold away. Similarly, if you double click on ‘UBX’, it will expand showing the various UBX sentences. By default, many of these are not enabled.
Resources and Going Further
U-blox 7 Download
Ready to get hands-on with GPS?
We've got a page just for you! We'll walk you through the basics of how GPS works, the hardware needed, and project tutorials to get you started.
We only went over a few of the features with the u-center. For more resources, we recommend checking your module's protocol specification and the u-center's documentation for more information.
- u-blox u-center Downloads
Once you've mastered U-Center you're ready to begin configuring your Ublox module! Check out some of these related tutorials:
Building an Autonomous Vehicle: The Batmobile
GPS-RTK Hookup Guide
GPS-RTK2 Hookup Guide

Setting up a Rover Base RTK System
How to Build a DIY GNSS Reference Station
U-blox 7 Driver




